Interaction between Living Things
Would you be surprised to know that we have the same necessities as a fly, a frog or a tree to be alive?
- Water: cells of living things are made of 70% water.
- Not all living things drink water. Let´s think about camels. Camels do not drink water during winter season; they take water form the leaves they ate, but in summer they can drink up to 190 L of water at once.
- Air is a mixture of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Living things use oxygen in the chemical process that releases ENERGY from FOOD
- Some living things do not need oxygen. They are called anarobic organisms, such as Clostridium botulinum a bacteria which makes us ill .
- Place to live: habitat or ecosystems must have all things living things need to survive. For instance, elephants needs a lot of sapce and food.
Food: organisms use food to get ENERGY to develop the essential processes of life and to build structures.
Space on Earth is limited so organisms often compete with each other for food, water, space.Let´s see how this is working. Visit the following web site and play the population game to see how abiotic and biotic factors affect rabbits population.
Population game
http://www.abpischools.org.uk/page/modules/population_growth/activity.cfm
Energy transfer through food
Organisms can be grouped into three different goups based on how they get their food:
Producers: Plants are called producers. This is because they produce their own food. They do this by using light energy from the Sun, carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil to produce food: in the form of glucose/sugar:
The porcess is called PHOTSYNTHESIS:
The porcess is called PHOTSYNTHESIS:
Consumers: animals are called consumers. This is because they cannot make their own food, so they need to consume (eat) plants and/or animals. There are three groups or cosumers: Herbivores (eat only plants), carnivores (eats only animals) and ominoveres (eats both plants and animals).
Decomposers
Bacteria and fungi are decomposers. They eat decaying matter - dead plants and animals and in the process they break them down and decompose them When that happens, they release nutrients and mineral salts back into the soil - which then will be used by plants!
Now let´s see how much you´ve learned
http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/content/animals/kidscorner/games/producersconsumersgame.htm
FOOD CHAIN
- Food Chain: the sequence of these eat and be eaten relationships
- It starts with a producer and ends with a consumer.
Trophic level: a
position in a food chain occupied by a group of organisms with similar food
mode.
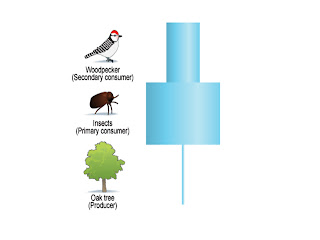
•Pyramid of numbers: the
population of each organism in a food chain can be shown in a bar chart called pyramid of numbers.
•The
producer always goes at the bottom.
Sometimes the pyramid of numbers doesn't look like a pyramid at all.
This is because the pyramid chart shows the biomass of the polupation: the weight of each organism in the food chain.
Then, this could happen if the producer is a large plant
such as a tree, or if one of the animals is very small, like the insect shown above.
such as a tree, or if one of the animals is very small, like the insect shown above.
An oak tree is very large so many insects can feed on it
Food webs
When
all the food chains in a habitat are joined up
together they form a food web
Let´s think about this food web:
How many producers are? Just one: the grass
How many predators? There are 5 predators: frog, vole, thrush, hawk and the fox
How many consummers? there are 8 consummers. Everyone is eating, but the grass (the producer)
and how about the number of preys? There are 6 preys: rabbit, insect, slug, frog, vole and thrush. The grass is not a prey and the top predators: the hawk and the fox are not preys.
could you tell how many herbivores are in the food web? there are 3 herbivores (eating plants): the rabbit, insect and the slug.
and how many carnivores? there are 5 carnivores: frog (eating insects), vole (eating insects), thrush eating slugs), fox (eating rabbit, voles and frogs) and the hawk (eating frogs, voles and thrushes)
Who´s the top predator? there are two: the fox and the hawk
what would happen if there were no grass?
•The grass is the producer, so if it died the consumers that feed on it: rabbits, insects and slugs - would have no food.
How many producers are? Just one: the grass
How many predators? There are 5 predators: frog, vole, thrush, hawk and the fox
How many consummers? there are 8 consummers. Everyone is eating, but the grass (the producer)
and how about the number of preys? There are 6 preys: rabbit, insect, slug, frog, vole and thrush. The grass is not a prey and the top predators: the hawk and the fox are not preys.
could you tell how many herbivores are in the food web? there are 3 herbivores (eating plants): the rabbit, insect and the slug.
and how many carnivores? there are 5 carnivores: frog (eating insects), vole (eating insects), thrush eating slugs), fox (eating rabbit, voles and frogs) and the hawk (eating frogs, voles and thrushes)
Who´s the top predator? there are two: the fox and the hawk
what would happen if there were no grass?
•The grass is the producer, so if it died the consumers that feed on it: rabbits, insects and slugs - would have no food.
They would starve and die unless they could move to
another habitat
Some
animals can just eat more of another organism if food is in short supply, while
others may starve and die.
This
in turn can affect the populations of other organisms in the food web.










No hay comentarios.:
Publicar un comentario